
Understanding Bios Blood Pressure Monitors
Bios monitors aid in tracking health, offering features like memory storage and irregular heartbeat detection; proper use ensures reliable data for informed decisions.
What is a Bios Blood Pressure Monitor?
Bios blood pressure monitors are sophisticated medical devices designed for convenient and accurate home blood pressure measurement. Unlike traditional manual methods requiring a stethoscope and skilled auscultation, Bios devices utilize oscillometric technology – sensing pressure fluctuations within your arteries. These monitors typically feature a digital display, presenting systolic and diastolic readings, alongside pulse rate.
They empower individuals to proactively manage their cardiovascular health, tracking trends over time. Many Bios models incorporate advanced functionalities like memory storage for multiple users, irregular heartbeat detection, and connectivity to mobile applications for data analysis and sharing with healthcare professionals.
Types of Bios Blood Pressure Monitors Available
Bios offers a diverse range of blood pressure monitors to suit individual needs. Upper arm monitors, considered more accurate, utilize a cuff placed around the upper arm. Wrist monitors provide convenience and portability, ideal for travel, though positioning is crucial for reliable results.
Furthermore, Bios categorizes models by features: basic monitors display readings, while advanced versions include Bluetooth connectivity for smartphone syncing, memory for multiple users, and irregular heartbeat alerts. Some even offer specialized modes for pregnancy or specific health conditions, enhancing personalized health management.
Preparing for Your First Measurement
Ensure a calm environment, avoid caffeine/exercise 30 minutes prior, and sit comfortably with supported back and feet flat for accurate readings.
Correct Positioning for Accurate Readings
Achieving precise blood pressure measurements hinges on proper positioning. Sit upright in a chair with back support, ensuring your feet are flat on the floor – avoid crossing your legs. Your arm should be supported at heart level, ideally on a table.
Relax your arm and avoid tension. The cuff should be placed directly on bare skin, not over clothing. Maintain a quiet environment, free from distractions, and refrain from talking during the measurement process. Allow several minutes of rest before taking readings to ensure stability and accuracy. Consistent positioning is key for reliable tracking.
Choosing the Right Cuff Size
Selecting the appropriate cuff size is crucial for accurate blood pressure readings. A cuff that’s too small will yield falsely elevated results, while one that’s too large can produce artificially low readings. Measure your arm circumference midway between your elbow and shoulder.
Most Bios monitors come with a standard cuff, but alternative sizes are often available. Consult the monitor’s manual or the Bios website to determine the correct size based on your arm measurement. Ensure the cuff’s bladder encircles at least 80% of your arm’s circumference for optimal precision.
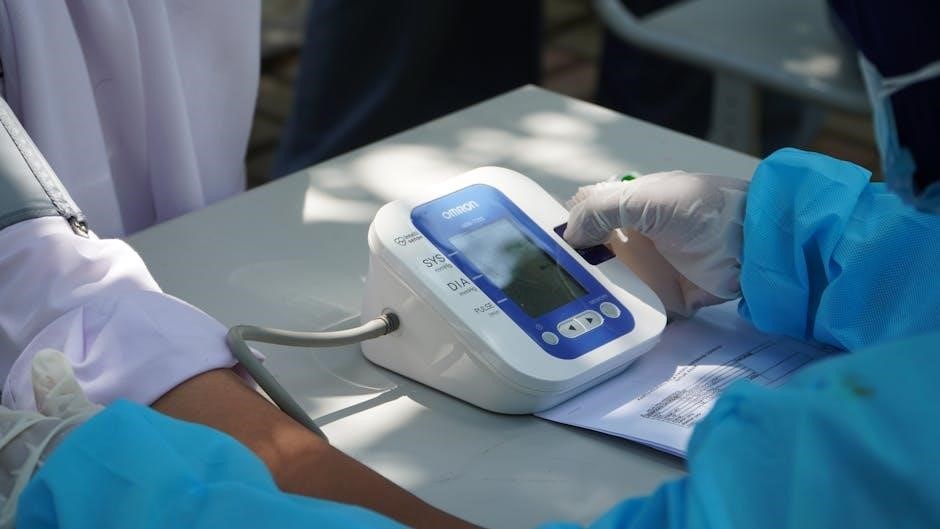
Taking a Blood Pressure Measurement
Ensure a relaxed state, sit upright, and position the cuff correctly on your bare arm for a precise reading using your Bios device.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Monitor
First, power on the Bios monitor and ensure the cuff is correctly connected. Position yourself comfortably with your back supported and feet flat on the floor. Apply the cuff snugly to your upper arm, approximately one inch above your elbow, ensuring the artery marker aligns with your brachial artery.
Press the start button and remain still and silent throughout the measurement process. The cuff will inflate automatically, and after a short period, it will deflate while displaying your systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings, along with your pulse rate. Record these values for tracking and potential consultation with your healthcare provider.
Understanding the Display Symbols
The Bios monitor’s display utilizes various symbols for clear communication. A heart symbol indicates pulse rate, measured in beats per minute. Systolic pressure, the top number, represents pressure during heart contraction, while diastolic, the bottom number, shows pressure when the heart rests.
Error symbols signal issues like cuff disconnection or movement during measurement; consult the manual for specific troubleshooting. An irregular heartbeat symbol alerts you to potential arrhythmias, prompting medical evaluation. Battery level indicators show remaining power, and memory symbols confirm data storage status. Familiarizing yourself with these symbols ensures accurate interpretation.

Interpreting Your Blood Pressure Readings
Readings reveal cardiovascular health; systolic/diastolic values categorize pressure as normal, elevated, or high, guiding lifestyle adjustments and medical consultations.
What are Systolic and Diastolic Numbers?
Blood pressure is recorded as two numbers: systolic and diastolic, expressed as systolic/diastolic (e.g., 120/80 mmHg). Systolic pressure represents the force against artery walls during heart contraction when the heart beats and pumps blood. Diastolic pressure measures the force against artery walls between heartbeats, when the heart muscle relaxes.
Understanding both values is crucial. Elevated systolic pressure often indicates stiffening of arteries with age, while high diastolic pressure can signify increased resistance in blood vessels. Consistent monitoring, using a Bios monitor, provides valuable data for assessing cardiovascular health and identifying potential risks, enabling proactive management and informed medical discussions.
Blood Pressure Categories: Normal, Elevated, and High
Blood pressure readings fall into categories guiding health management. Normal pressure is less than 120/80 mmHg. Elevated readings range from 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic. High Blood Pressure, or Hypertension, starts at 130/80 mmHg or higher, categorized further into stages.
Regularly using a Bios blood pressure monitor helps track these categories. Consistent elevated readings warrant lifestyle changes and potential medical intervention. Understanding your category empowers proactive health decisions, facilitating timely consultations with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and effective blood pressure control.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Error messages indicate problems like cuff disconnection or movement during readings; inaccurate results may stem from improper cuff size or positioning—review the manual.
Error Messages and What They Mean
Bios blood pressure monitors utilize error codes to signal issues during measurement. An “Err” or “E” display often indicates movement during the reading – remain still! A cuff error signifies a disconnected or improperly fitted cuff; ensure secure attachment. Low battery power triggers a battery symbol, requiring replacement. Irregular heartbeat symbols don’t necessarily indicate a problem, but warrant medical consultation if frequent. Always consult the device’s manual for specific code definitions, as variations exist between models. Ignoring error messages can lead to inaccurate readings and compromised health monitoring. Addressing these promptly ensures reliable data and effective blood pressure management.
Inaccurate Readings: Causes and Solutions
Bios monitor inaccuracies stem from several factors. Incorrect cuff size is a primary culprit – ensure a proper fit. Movement during measurement drastically alters results; remain still and relaxed. Improper positioning, like crossing legs, impacts readings. Defective batteries or a malfunctioning monitor can also cause errors. Retake the measurement after a few minutes, ensuring correct technique. If inconsistencies persist, verify the monitor’s calibration or consider a replacement. Regularly compare readings with a manual check at a doctor’s office to validate accuracy and maintain reliable health data.

Maintaining Your Bios Blood Pressure Monitor
Regular cleaning with a soft, dry cloth preserves accuracy. Store the monitor safely, avoiding extreme temperatures and humidity, and replace batteries promptly.
Cleaning and Storage Instructions
To ensure the longevity and accuracy of your Bios blood pressure monitor, regular cleaning is essential. Always disconnect the cuff and power source before cleaning. Gently wipe the monitor’s surface with a soft, slightly damp cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals, abrasive cleaners, or excessive water, as these can damage the device.
For storage, keep the monitor in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Avoid storing it in humid environments. Protect the cuff from sharp objects and ensure it’s not bent or twisted excessively. Proper storage will help maintain the monitor’s functionality and provide reliable readings for years to come.
Battery Replacement Guide
When the low battery indicator appears on your Bios blood pressure monitor, it’s time for a replacement. Typically, these monitors require AA or AAA batteries. Locate the battery compartment, usually on the back or bottom of the device, and gently open it. Remove the old batteries, noting the correct polarity (+ and -) indicated inside the compartment.
Insert fresh batteries, ensuring proper alignment with the polarity markings. Close the battery compartment securely. Dispose of used batteries responsibly, following local regulations. Replacing the batteries will restore full functionality to your monitor, ensuring accurate blood pressure measurements.

Advanced Features & Settings
Explore memory recall for tracking trends, and utilize irregular heartbeat detection for enhanced monitoring; customize settings for personalized, insightful health management.
Memory Function and Data Review
Bios blood pressure monitors commonly feature a memory function, allowing storage of numerous readings for comprehensive tracking. This stored data enables users and healthcare professionals to identify patterns and trends in blood pressure over time. Accessing this data is typically straightforward, often involving a dedicated “Memory” or “Recall” button on the device.
Reviewing past readings can help determine the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medication adjustments. Many models display average readings, providing a quick overview of blood pressure control. Some Bios monitors also allow data transfer to computers or mobile devices for more detailed analysis and reporting, facilitating better health management.
Irregular Heartbeat Detection
Many Bios blood pressure monitors incorporate irregular heartbeat (IHB) detection, a valuable feature for identifying potential arrhythmias. During a measurement, the monitor analyzes your pulse for inconsistencies. If an irregular rhythm is detected, a symbol typically appears on the display alongside your blood pressure readings.
It’s crucial to understand that IHB detection isn’t a diagnosis; it simply indicates a potential irregularity. If the monitor frequently displays the IHB symbol, consult your doctor for a proper evaluation, including an electrocardiogram (ECG), to determine the cause and appropriate course of action.
Connecting to Mobile Apps & Software
Bios monitors often pair via Bluetooth, enabling data synchronization with smartphone apps for tracking trends and sharing information with healthcare providers.
Bluetooth Pairing Instructions
To connect your Bios blood pressure monitor to a mobile device via Bluetooth, first ensure Bluetooth is enabled on your smartphone or tablet. Open the Bios app and navigate to the device settings or pairing section. Put the monitor into pairing mode – typically by pressing and holding a specific button on the device itself, as detailed in your user manual.
The app will then search for available devices. Select your Bios monitor from the list when it appears. You may be prompted to enter a pairing code, usually displayed on the monitor’s screen or within the app. Confirm the pairing request on both devices. Once successfully paired, data will automatically synchronize, allowing for convenient tracking and analysis of your blood pressure readings.
Data Synchronization and Analysis
Once your Bios blood pressure monitor is paired with your mobile device, data synchronization occurs automatically after each measurement. The Bios app compiles your readings, presenting them in easy-to-understand graphs and charts. You can view historical data by day, week, or month, identifying trends and patterns in your blood pressure.
The app often provides insightful analysis, highlighting average readings and potential irregularities. Some apps allow exporting data to share with your healthcare provider. Regularly reviewing your data empowers you to proactively manage your health and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Medical Considerations
Consult a doctor for readings outside the normal range, or if you have kidney disease or heart failure; regular monitoring aids management.
When to Consult a Doctor About Your Readings
It’s crucial to understand when your blood pressure readings necessitate medical attention. Consistently high readings, even with home monitoring, warrant a doctor’s visit for evaluation and potential treatment adjustments. Seek immediate medical advice if you experience severely elevated blood pressure accompanied by symptoms like severe headaches, nosebleeds, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
Furthermore, if you notice a sudden and significant change in your blood pressure, or if the monitor consistently displays error messages, consult your physician. Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure, should regularly share their blood pressure data with their healthcare provider for optimized management.
Blood Pressure Monitoring for Specific Conditions (Kidney Disease, Heart Failure)
For individuals with kidney disease, consistent blood pressure control is paramount to slowing disease progression. Regular monitoring with a Bios monitor allows for close tracking and adjustments to medication as needed, guided by your physician. Similarly, in heart failure, maintaining optimal blood pressure is vital for reducing strain on the heart.
Frequent monitoring helps manage fluid balance and assess the effectiveness of treatments. Share readings regularly with your doctor; they may adjust your medication or lifestyle recommendations based on trends observed. Accurate data empowers proactive healthcare management for these conditions.
Resources and Support
Bios offers comprehensive online FAQs and a dedicated customer support team to assist with any questions regarding monitor operation or data interpretation.
Bios Official Website and FAQs
Bios’ official website serves as a central hub for all product-related information, including detailed manuals, troubleshooting guides, and frequently asked questions. Users can access step-by-step instructions on setting up and operating their specific Bios blood pressure monitor model. The FAQ section addresses common concerns regarding cuff placement, error messages, data interpretation, and connectivity issues with mobile apps.
Furthermore, the website provides downloadable resources, such as quick start guides and software updates. Regularly checking the website ensures access to the latest information and support materials, maximizing the benefits of your Bios device and promoting accurate blood pressure monitoring.
Customer Support Contact Information
Bios offers multiple channels for customer support, ensuring assistance is readily available when needed. Users can reach the support team via phone during business hours for immediate help with operational questions or troubleshooting. An email support option provides a convenient way to submit detailed inquiries and receive personalized guidance regarding Bios blood pressure monitor usage.
Additionally, a live chat feature on the official website offers real-time assistance. For self-service support, a comprehensive knowledge base and online forum provide answers to frequently asked questions and allow users to connect with other Bios product owners.